Introduction
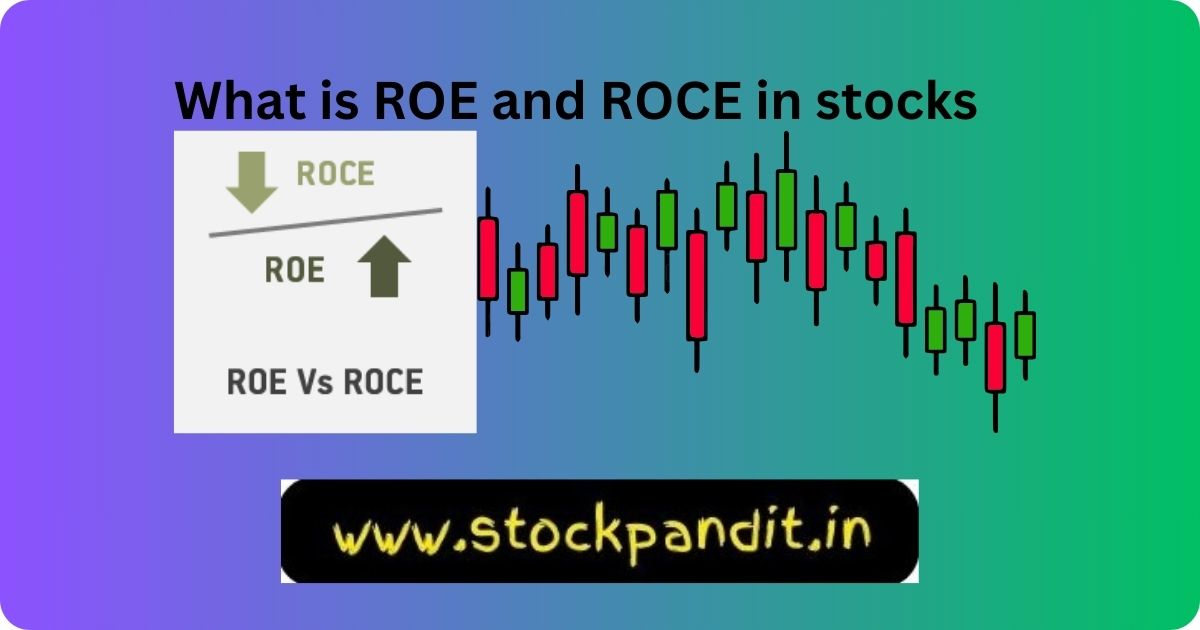
Definition of ROE and ROCE
Understanding of What is ROE and ROCE in stocks: ROE (Return on Equity) measures a company’s profitability by showing how much profit it generates relative to the shareholder equity.
ROCE (Return on Capital Employed) evaluates a company’s efficiency in using its capital to generate profits. It’s calculated by dividing Earnings Before Interest and Tax (EBIT) by Capital Employed.
Importance in Stock Market
These metrics are vital for investors as they provide insights into a company’s financial health and efficiency in using funds.
You May Also Like: NPA Meaning in Banking
Understanding ROE
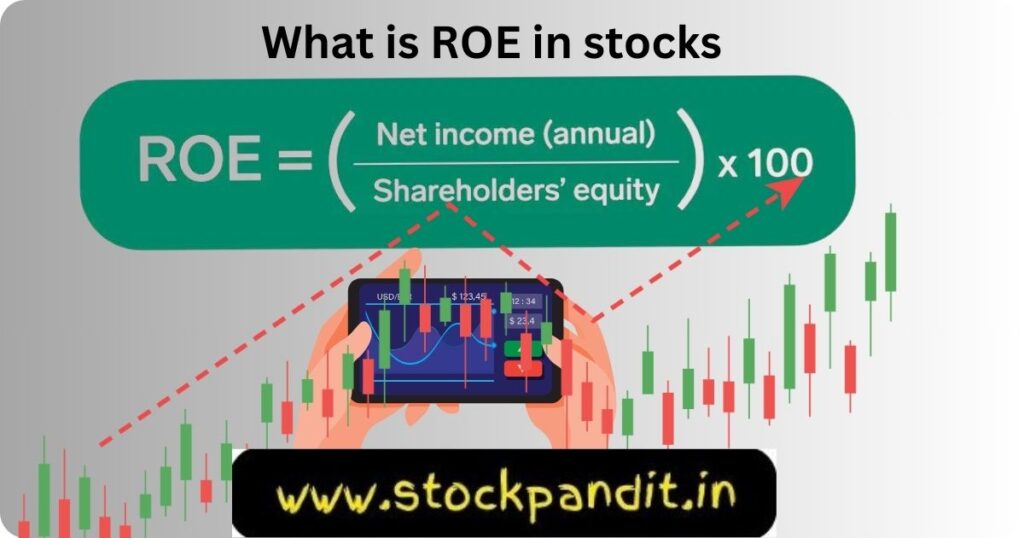
ROE stands for Return on Equity, a financial measure that reflects how profitable a company is in relation to the equity invested by shareholders. It assesses how effectively a company utilizes its equity to generate profits. To calculate ROE, divide a business’s net profit by the shareholders’ equity.
For instance, if a company has a net income of Rs. 100 and the equity is Rs. 500, the ROE would be 20 percent (100/500). This metric is significant for investors as it showcases the company’s ability to generate profit per unit of investment.
A high ROE often signifies effective utilization of resources, but it doesn’t guarantee investment success. Context, such as the company’s financial health and industry performance, is essential when evaluating ROE. Comparing ROE between companies within the same industry helps investors make informed decisions.
While ROE is a vital metric for investment consideration, it should be analyzed alongside other financial indicators and qualitative factors like operations, industry trends, and competitive landscape to gain a comprehensive understanding of a company’s potential for investment and financial well-being.
You May Also Like: How to Learn Trading-Avoid 5 Mistakes
Explaining ROE
ROE essentially shows how effectively a company generates profits based on the money invested by shareholders. A high ROE indicates efficient use of equity.
Significance in Stocks
In the stock market, ROE is a key metric used to assess a company’s performance. It helps investors gauge profitability and compare different companies in the same industry.
Interpreting ROE
When interpreting ROE, consider the industry average. Comparing a company’s ROE to its peers can provide insights into its competitiveness and operational efficiency.
Understanding ROCE
Defining ROCE
ROCE evaluates how well a company utilizes both equity and debt to generate profits. A higher ROCE typically suggests better capital utilization.
Role in Investment
For investors, ROCE is crucial as it indicates the efficiency of the company’s investments and its ability to generate returns from the capital employed.
You May Also Like: How to Invest in Nifty 50 ETF 2024
Comparing ROE vs. ROCE
ROE focuses solely on equity, while ROCE considers all forms of capital employed. Both metrics offer distinct perspectives on a company’s performance.

Application in Stock Investing: What is ROE and ROCE in stocks ?
ROE and Stock Selection
High ROE can attract investors seeking profitable companies. However, it’s essential to analyze other factors alongside ROE for a comprehensive assessment.
ROCE’s Impact
ROCE influences investment decisions by highlighting a company’s ability to generate returns from both equity and debt.
Differences and Considerations
ROE and ROCE Variations
Different industries have varying benchmarks for ROE and ROCE due to their capital structures and business models.
Limitations
While crucial, ROE and ROCE have limitations. They might not capture the complete financial picture of a company, so it’s vital to use them alongside other metrics.
Interpreting ROE and ROCE in Practical Scenarios
Case Studies
Real-life examples showcasing how these metrics impact stock performance can help investors understand their implications.
Analyzing Stocks
Demonstrating how to use ROE and ROCE when analyzing specific stocks can aid investors in making informed decisions.
Watch This YouTube Video For More Details
FAQs on ROE and ROCE:
FAQ 1: What’s a good ROE/ROCE value for a stock?
It varies across industries, but generally, higher than the industry average is favorable.
FAQ 2: How do ROE and ROCE differ from each other?
ROE measures profitability based on shareholder equity, while ROCE considers all capital employed.
FAQ 3: Can low ROE/ROCE indicate problems with a company?
Yes, it might indicate inefficiency in using capital or a need for further analysis.
FAQ 4: Should I prioritize ROE or ROCE when analyzing stocks?
Both metrics provide valuable insights; considering both is ideal.
FAQ 5: What factors can influence variations in ROE/ROCE for different companies?
Capital structure, industry dynamics, and operational efficiency are among the influencing factors.
FAQ 6: Are there industries where ROE/ROCE are less relevant?
Some industries with high capital requirements might have different key performance indicators.
Conclusion
Summarizing ROE and ROCE
Recapitulating the importance and application of ROE and ROCE in stock analysis.
Encouraging Further Research
Suggesting readers explore additional resources or seek professional advice for a more in-depth understanding.